

For example Octopictures are in a folder called 1998\10 October\19981016. You can also rename multiple files using PowerShell.I have 14,000 pictures sorted into files by year and month but taken with multiple cameras and I want the file name to reflect the date taken. To rename a single file using PowerShell, use the following command: Rename-Item -Path "\\fs\Shared\temp.txt" -NewName "new_temp.txt" You can also move an entire folder with PowerShell.

The Move-Item cmdlet moves an item, including its properties, contents and child items, from one location to another: Move-Item -Path \\fs\Shared\Backups\1.bak -Destination \\fs2\Backups\archive\1.bak
MASS RENAME FILES USING POWERSHELL HOW TO
Learn how to overwrite files when copying them from or to a remote computer. Note that if the target file already exists, the copy attempt will fail. The following command creates a backup by copying the file users.xlsx from one remote computer (fs) and to another (fs2) over the network: Copy-Item -Path \\fs\Shared\it\users.xlsx -Destination \\fs2\Backups\it\users.xlsx Use the Copy-Item cmdlet to copy objects from one path to another. You can also delete all files older than X days or delete files from multiple computers with PowerShell. Confirmation will be requested upon execution if the object is not empty. To delete an object, use the Remove-Item cmdlet. You can also use the New-Item cmdlet to create files, folders or registry keys To create a new directory with PowerShell, use the New-Item cmdlet: New-Item -Path '\\fs\Shared\NewFolder' -ItemType Directory You can use the New-Item cmdlet to create files, folders, directories and registry keys.
MASS RENAME FILES USING POWERSHELL WINDOWS
To create a new object with Windows PowerShell, use the New-Item cmdlet and specify the type of item you want to create, like this: New-Item -Path '\\fs\Shared\NewFolder\newfile.txt' -ItemType File You can also use the New-Item cmdlet to create folders, directories or registry keys. Use the New-Item cmdlet to create a file: New-Item -Path '\\fs\Shared\NewFolder\newfile.txt' -ItemType FileĬreating a file overwrites any existing one with the same name, so you might need to check whether the file already exists. Using the information in this article, you can automate a variety of simple operations related to file management on your file storages and save time for more important tasks. Get-ADComputer -Filter * | Export-Csv -Path C:\data\pc.txtĮlse

#if matching return “True” key then exit, if “False” then create a report $files=Get-ChildItem C:\data\*.txt | select -expand fullname The following script checks whether a specific file (pc.txt) already exists in a particular folder if not, it generates a list of all AD computers and saves it to a new file named pc.txt: #create array of text files You can also create files using the Export-Csv cmdlet, which exports the output into a csv file that can be opened in Excel: Get-ADuser -Filter * | Export-Csv -Path C:\data\ADusers.csv Create files after checking that they don’t already exist To overwrite an existing file, use the –Force switch parameter.
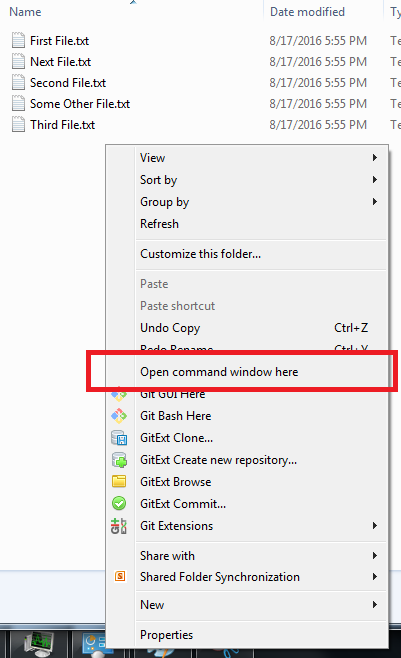
The first is to use the Out-File cmdlet: $text = 'Hello World!' | Out-File $text -FilePath C:\data\text.txt There are at least two built-in methods to create a file and write data to it. To create new objects with Windows PowerShell, you can use the New-Item cmdlet and specify the type of item you want to create, such as a directory, file or registry key.įor example, this command creates a folder: New-Item -Path '\\fs\Shared\NewFolder' -ItemType DirectoryĪnd this command creates an empty file: New-Item -Path '\\fs\Shared\NewFolder\newfile.txt' -ItemType File Create files and writing data to them


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
